Thought leadership
– 13 min read
Why AI-native enterprise apps are the business brain of the future

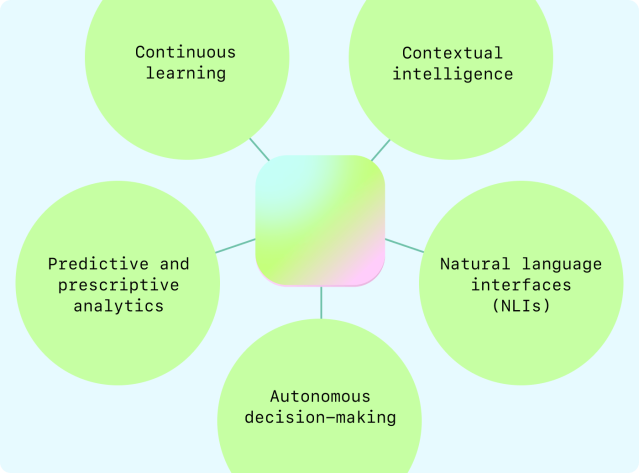
AI-native enterprise apps are fundamentally changing the way businesses work by integrating AI into their core, making them smart, predictive, and adaptable. They improve decision-making and operational efficiency with features like contextual intelligence, natural language interfaces, predictive analytics, autonomous decision-making, and continuous learning. They impact different business functions, like customer service, sales, HR, and finance, by enabling real-time data analysis and personalized strategies. WRITER is leading this change, helping organizations use AI-native apps to transform their operations.
The first three industrial revolutions — steam, electricity, and computers — changed the world over centuries. The fourth revolution, driven by AI, did it in mere years. Today, AI is changing the way we do business by the minute. As Henry Bristol et al. at McKinsey put it, “AI has brought the Fourth Industrial Revolution to an inflection point, and [businesses] must choose a path forward: innovate, accelerate, or follow fast.”
The exponential growth in AI capabilities is fundamentally restructuring how we architect enterprise software. If you’re a business wondering how to implement AI into your software, you’re already too late. We’ve moved beyond AI as a bolt-on feature. It’s no longer about upgrading software with AI. It’s about accelerating workflows, reimagining business models, and fundamentally changing how we work.
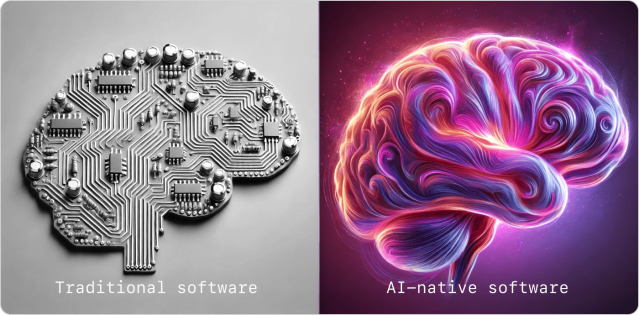
AI-native apps are quickly becoming an evolving and learning business “brain.” This “brain” is baked into the very business DNA, improving every aspect of business operations — from human resources to sales and marketing, technology, and production.
AI-native app features accelerate workflows by combining contextual awareness and autonomous decision-making
What if software truly understood what you need to get done? AI-native apps do exactly that. They’re your intelligent co-pilot who gets the terrain of your business operations, makes smart decisions on the fly, and adjusts to any sudden changes in data or processes — so you can free yourself from the grind of daily tasks.
Contextual intelligence
Working with an app without contextual intelligence is like starting from scratch every time. You have to rebuild the context, explain your preferences, and give it all the background information again and again. It’s a huge time waste and a frustrating experience for the user.
Contextual intelligence is the app’s awareness of the query context. It understands what the user wants, recognizes historical data trends, and considers environmental factors.
For example, if you ask it to pull data from a CRM, it’ll know which fields and filters you typically use, saving you lots of time. It can even help with decisions by adapting to your behavior and routine actions. Say, you want to update financial records. The app can automatically categorize your expenses based on past entries, or even predict your future spending trends. It’s like an accountant who knows your financial habits and goals.
Contextual intelligence can simplify tasks like sending emails (by auto-filling recipients and suggesting relevant content), generating XML reports (by using templates and data sources you’ve used before), or launching campaigns (by recommending strategies that have worked in similar contexts). It can even help with coding by suggesting functions or modules based on what you’re currently working on.
Natural language interfaces (NLIs)
Natural language interfaces (NLIs) are user interfaces that let users interact with the app by using everyday language. NLIs use natural language processing (NLP) and natural language understanding (NLU) to understand and reply to the user’s query in a human-like manner. It’s like creating a more human software, one that understands us and can adapt to our needs.
Imagine asking your ERP system, “What’s our inventory situation for Product X in Region Y?” and receiving an instant, comprehensive answer. The app understands the context, and the conversation is natural, with a natural back-and-forth exchange like clarifying questions, suggestions, or additional prompts. You feel like you’re chatting with a colleague who knows exactly what you need.
One of the biggest advantages of NLIs is that they don’t need menus or buttons, making apps more accessible and super easy to use, especially for non-technical users. Let’s say a new employee needs to navigate a complex enterprise system. With an NLI, they can simply ask, “How do I update financial records?” and the app will guide them through the process step by step. Then they can say, “Send an email to the sales team with the latest revenue forecast,” and the app will draft the email, attach the relevant report, and send it off without the employee having to lift a finger.
Predictive and prescriptive analytics
We’re moving from “What happened?” to “What will happen, and what should we do about it?” AI native apps will be better at predicting and prescribing solutions, making them particularly useful in areas like sales and inventory management. They can analyze data to forecast trends and suggest actions that align with business goals, changing how we approach decision-making.
To forecast trends, predictive analytics use statistical algorithms, machine learning (ML) models, and historical data. For example, an AI-native healthcare app can predict if a patient is at risk of developing a certain condition based on their medical history. By using predictive analytics, the app can alert healthcare providers to potential health issues before they become critical, enabling proactive care and better patient outcomes.
Prescriptive analytics go a step further. The app can suggest actions based on the outputs predicted by predictive analytics, offering insights that drive business decisions. For example, an AI-native marketing app can recommend a discount for customers who are likely to buy a product based on their purchase history. By understanding customer behavior and preferences, the app can suggest strategies that maximize engagement and conversion rates.
Together, predictive and prescriptive analytics identify potential outcomes and help plan the best way forward. If predictive analytics are like a weather forecast, cautioning you about a storm, then prescriptive analytics are like a GPS, telling you how to get to your destination.
Autonomous decision-making
AI-native apps aren’t just prescriptive. They actively drive your operations forward by making intelligent decisions on their own. With advanced tool and function calling capabilities, they can interact with external software, databases, and other enterprise tools — analyzing data, recognizing patterns, and making predictions based on that analysis.
For example, the app can automatically suggest corrections and improvements to written content, ensuring grammatical accuracy, clarity, and adherence to a company’s style guide. This is done through real-time analysis of the text, using NLP techniques. Or it can generate content autonomously, like drafting emails, creating blog post outlines, and even creating UI copy. This is achieved by understanding the context and intent of the user’s input and using that information to produce relevant and coherent text.
The app also makes decisions on its own when it comes to transparency and accountability. Techniques like SHAP (SHapley Additive exPlanations) and LIME (Local Interpretable Model-agnostic Explanations) help us understand decision-making processes of the AI models — improving transparency and trust.
Plus, models can mitigate bias through various mechanisms, like data cleaning, model auditing, and fine-tuning with human feedback. This makes sure that the autonomous decisions made by the app are fair and unbiased.
Continuous learning
AI-native apps thrive on continuous learning. Compared to traditional models that are trained on a static data set, deployed, and have to be periodically re-trained, AI-native apps learn from the user’s interaction patterns, changing business environments, and new data streams to improve in real-time.
Consider how these apps adapt to new patterns and changes in data. They make small, frequent adjustments rather than big, infrequent updates. This is important for apps where fresh data can improve timeliness and accuracy — like fraud detection systems or predictive maintenance tools. By incorporating feedback loops, AI-native apps use the outcomes of previous actions to improve future decisions, avoiding the issue of catastrophic forgetting where models lose prior knowledge when learning new tasks.
A practical example of this in action is an AI-powered marketing platform we deployed last year. Through continuous learning from campaign data, it increased its predictive accuracy by 27%. It adapted in real-time to shifts in consumer behavior, market trends, and campaign performance metrics. This not only improved the effectiveness of marketing efforts but also reduced the need for constant manual updates.
And for developers, continuous learning means less time spent on maintenance and more time on coding and innovation.
AI-native apps are built with AI as the foundation — not tacked on as a feature
When AI is embedded into the foundation of an app as opposed to being tacked on like a plugin, it stops being a tool. It becomes a business partner. Think of it as a superpower that creates a mutually beneficial AI-human relationship. The app is there to do the heavy “data” lifting, so that the business user can focus on strategy, creativity, and simply doing their job.
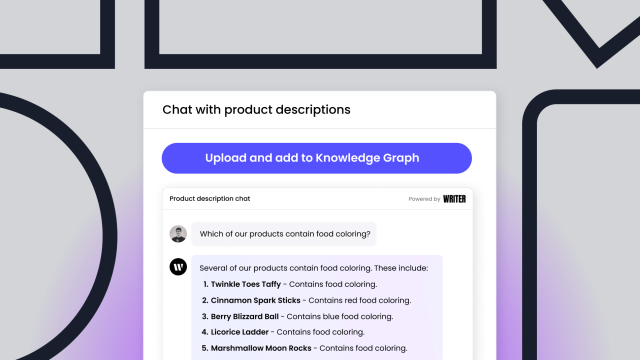
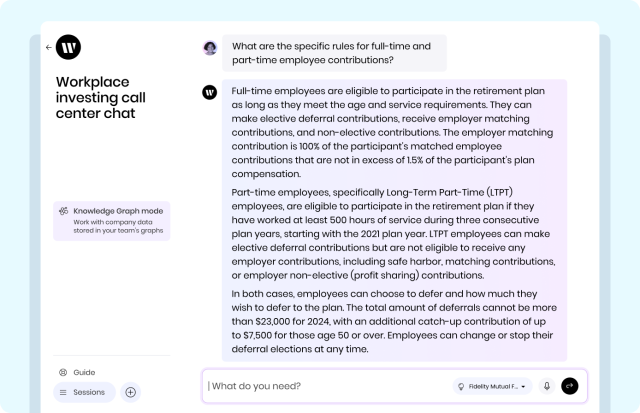
Let’s say, a support agent working for Fidelity gets on the phone with a customer who has signed up for Fidelity 401k and is asking about specific rules for full-time and part-time employee contributions. Normally, an agent would have to go into a SharePoint environment and manually search through multiple documents, which can take 20 minutes or longer. With an AI-native app, the agent can query the Knowledge Graph, understand all available options, and tell the customer the correct answer live — all within a few minutes.
This fast response is possible because AI-native apps are built from the start with AI technologies like machine learning (ML), natural language processing (NLP), and computer vision. They can learn, adapt, and improve on their own — eliminating the need for developers to update them manually. These apps can perform difficult tasks like predictive analysis, pattern recognition, and decision-making. Additionally, since they’re often cloud-based, they can scale up to handle massive enterprise-level datasets.
By baking AI into the app’s very architecture, enterprises can get a serious edge ahead of the competition. Think optimizing operations, improving user experience, and introducing a fundamentally new way to handle data-driven tasks. In short, AI-native apps are built to grow with the business. This kind of adaptability makes them not just useful but a must for every enterprise environment.
AI-native apps manage data and make decisions in real-time
AI-native apps are designed to handle vast amounts of data and make instant decisions. What’s really exciting is how they can adjust parameters on the fly. They ingest data from user interactions, sensors, and other apps, and process it instantly.
But ingestion is just the beginning. Through adaptive algorithms, apps adjust their internal parameters based on incoming data and ML insights. So a marketing platform can automatically adjust ad spend by analyzing real-time campaign performance metrics. If an ad is performing well, the app can increase its budget to maximize reach. But if an ad is performing poorly, the app can reallocate funds to more effective campaigns.
Even better, AI-native apps can adapt to different situations by understanding the context in which they’re operating. So a healthcare app can analyze a patient’s data like vital signs, lab results, and medical history, and adjust treatment plans in real-time. If a patient’s condition changes, the app recognizes this and recommends adjustments to their care plan with personalized medical advice. Similarly, a project management app can assign project tasks, reallocating resources and updating deadlines based on team availability and shifting priorities.
But perhaps the most transformative capability of AI-native apps is their ability to predict disruptions before they happen. Through advanced pattern recognition, they can analyze historical and current data to identify trends that could lead to future issues. For example, a manufacturing app can detect unusual machine behavior that could lead to a breakdown. A finance app can send alerts to stakeholders, alerting them to take action. Or a healthcare app can identify a patient’s health risks based on their vital signs and activity.
Finally, AI-native apps can suggest mitigation strategies. Through scenario analysis, they evaluate different options and recommend the best course of action. A supply chain app, for example, can suggest alternative shipping routes or different suppliers to avoid delays caused by unforeseen events like natural disasters or political unrest. Or a financial app can recommend investment adjustments to minimize risk during volatile market conditions.
Adopting AI-native apps results in benefits for both business and IT teams
AI-native apps are more than just software. They represent a strategic advantage that can transform operations and decision-making. As Paul Daugherty, Chief Technology and Innovation Officer at Accenture, writes, “The playing field is poised to become a lot more competitive, and businesses that don’t deploy AI and data to help them innovate in everything they do will be at a disadvantage.”
For enterprises, AI-native apps bring some serious benefits to the table. According to the 2024 Trends In AI report, “AI projects are driving significant business value, up from 28% last year.” AI apps can automate routine tasks and streamline workflows, which means your team can focus on higher-value activities. They’re also data powerhouses. They can analyze huge amounts of data quickly and accurately, providing insights for strategic decisions. Plus, they can help you understand your customers better, leading to improved customer experiences and increased loyalty.
From a developer’s perspective, AI-native apps can help with accelerating development cycles, automating code generation, testing, and debugging. Imagine having ML models that can identify and fix bugs instantly, or AI-driven code suggestions that improve your productivity. This means you can spend more time on complex and innovative aspects of your projects, leading to faster time-to-market for new features and products.
AI-native apps can also improve code quality and reliability. They use analytics and machine learning to detect issues early in the development cycle, analyze code for security vulnerabilities, and suggest best practices. This results in fewer bugs, better performance, and higher software quality overall.
AI-native apps already have a transformative impact on enterprise operations
AI-native apps touch every corner of the enterprise. As stated by McKinsey, “companies that have leading digital and AI capabilities outperform laggards by two to six times.”
Let’s take a look at a few examples:
- Customer service: Chatbots are old news. We’re now seeing AI systems that can handle complex, multi-step customer issues, even detecting and responding to emotional cues.
- Sales and marketing: AI is enabling hyper-personalization at scale. One customer saw a 40% increase in non-branded search using an AI system that tailors recommended product descriptions in real-time.
- Human resources: From predicting employee churn to personalizing development plans, AI is transforming HR into a strategic powerhouse.
The future is now
AI-native enterprise apps are reshaping what’s possible in business. They can intelligently interact with an entire enterprise ecosystem of tools, automate complex tasks and workflows, and compress innovation from decades to years — or even months.
Think data sharing and collaboration. Think personalized experience for every customer. Think an army of virtual experts for businesses in finance, health, retail, and technology that can bring new products and services to market faster than ever before.
At WRITER, we’ve been at the forefront of this revolution, helping our customers build truly AI-native apps. AI will fundamentally reshape how businesses operate — where collaboration between people and AI will be key — with AI designed to support rather than replace human roles.
Reach out to our team for a demo of some of the exciting AI-powered solutions we’ve developed. See firsthand how AI is changing enterprise software and discover how your organization can use these powerful technologies.