Innovation
– 19 min read
AI agents in the enterprise
What business leaders need to know
Picture this: You’re at the helm of a Fortune 500 company, feeling the weight of operational chaos, data silos, and inefficiencies. Now imagine a transformation so profound that, in just a few months, productivity doubles, costs plummet, and customer satisfaction soars. This isn’t a pipe dream — it’s soon to become the reality for businesses prepared to embrace AI agents.
Advancements in machine learning algorithms have accelerated the evolution of agentic AI. But SaaS providers and hyperscalers are currently over-promising the capabilities of today’s AI agents, creating confusion and unrealistic expectations among users and enterprise buyers alike. Many people assume that popular tools marketed as “AI agents” have advanced reasoning and sophisticated, multi-step problem-solving skills. And while such capabilities are on the horizon, they have yet to exist in the AI tools widely available to businesses today.
Consider this a clear, unhyped glimpse into the future of AI agents — and how to prepare your organization for their adoption. We’ll explore their capabilities, share practical implementation strategies, and reveal their significant impact on efficiency, decision-making, and competitive advantage in today’s dynamic business landscape. Let’s embark on this journey together and discover how AI agents can transform your enterprise in the months — and years — to come.
- AI agents automate tasks, enhancing enterprise operations and efficiency.
- AI agents provide benefits like cost savings, improved efficiency, better decision-making, and happier customers.
- Industries can leverage AI agents for tasks like automated data entry, patient record management, inventory management, and claims processing.
- Challenges include data governance, talent gap, cost and complexity, ethical dilemmas, and retraining needs.
- Successful deployment involves defining goals, providing tools, implementing feedback loops, ensuring human oversight, and managing risks.
What are AI agents?
AI agents, advanced software programs, use reasoning to accomplish goals. They’re a type of artificial intelligence (AI) that can perceive their environment and plan and take actions to achieve specific goals. These agents can operate independently, making decisions and performing tasks with minimal human intervention. This significantly improves enterprise operations.
AI agents operate based on predefined rules or machine learning algorithms, allowing them to analyze vast amounts of data and make informed decisions. They can perceive prompts, analyze the tools and data available, make a plan, and execute the plan by interacting with the models and tools needed to achieve a goal. Natural language processing plays a crucial role in this process, enabling AI agents to effectively interpret queries and generate relevant responses.
For example, let’s say a user prompts an AI agent with: “I’m traveling to San Francisco for a tech conference. What will the weather be like?”
The agent perceives the prompt and analyzes the tools and data available.
Then, it makes a plan:
- Ask the user what dates they’re traveling to San Francisco
- Call the weather API tool
- Check if the API response includes weather information about the location and travel dates
- If it does, generate a response with the new information
It executes the plan, interacting with the models and tools needed to achieve the goal.
Integrating AI agents into your operations can improve workflows, reduce errors, and improve overall efficiency. This frees up human resources to focus on more strategic and creative tasks, ultimately driving innovation and competitive advantage.
Categories of AI agent use cases for enterprises
The market has seen a significant increase in the number of AI agents being introduced, but the definitions and classifications of these agents are inconsistent, leading to a lot of confusion. There’s no universally accepted industry definition of an “AI agent” or who develops them.
Rather than getting caught up in these technical nuances, we encourage our customers to focus on the problem they need to solve and the solution that best fits. The goal isn’t to create the most advanced, autonomous agent—it’s to build one that works for the job at hand and aligns with your business objectives.
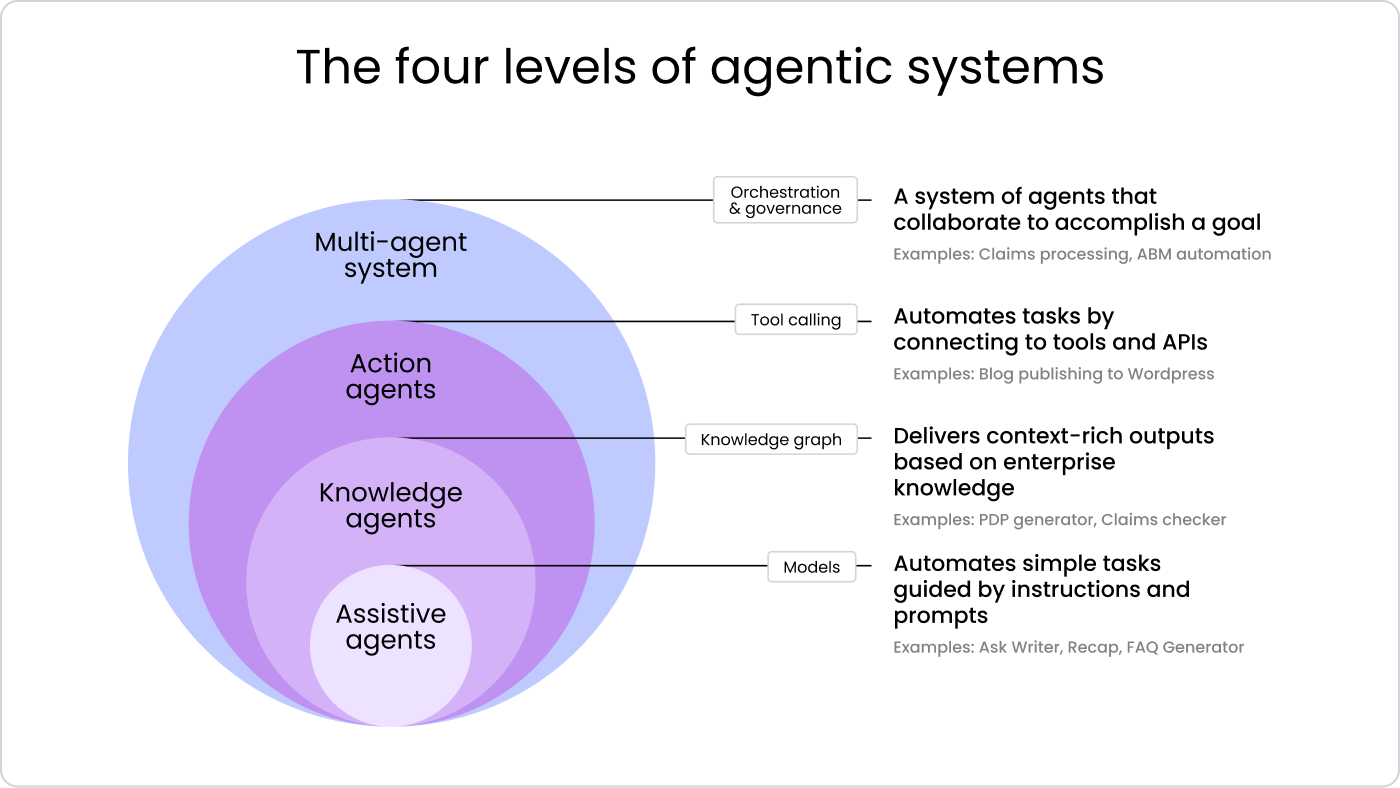
To help guide our customers, we’ve broken down enterprise AI agent use cases into four categories:
Assistive agent
An assistive agent uses language models (LLMs) to automate simple tasks based on instructions and prompts. The process is straightforward: input is fed into the LLM, which then generates the output. This type of agent doesn’t require external data or actions, making it ideal for tasks like recapping information or generating FAQs.
Knowledge agent
A knowledge agent delivers context-rich outputs by integrating enterprise knowledge. The process involves enriching the context via retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) before the LLM generates the output. This agent retrieves relevant information from internal documents and databases to provide more informed and contextually accurate responses.
Action agent
An action agent automates tasks by connecting to external tools and APIs. The LLM uses tool calling, which arms it with capabilities beyond its built-in knowledge, like allowing it to interact with third-party services to send an email or update a Salesforce record. This type of agent is useful for tasks that require interaction with your systems, such as publishing content to a platform like WordPress.
Multi-agent system
A multi-agent system involves a network of agents that collaborate to accomplish a goal. The process starts with an input, which is processed by the LLM, and then multiple agents work together to orchestrate the work. These agents communicate, pass tasks, and execute in a coordinated manner, making them ideal for complex workflows. For example, agents coordinating to process a full procurement workflow or resolve IT incidents end-to-end.
With these four categories, you can match the right kind of agent to the right problem. For those just getting started on your agentic AI journey, you can take a “crawl, walk, run” approach, progressively increasing the sophistication of your agents as you learn what works best for your use case.
Current approaches to AI agents for enterprise
Many enterprises are grappling with the friction between business and IT teams. This disconnect often arises because most AI tools force teams to make trade-offs: speed versus customization, flexibility versus control, or ease of use versus technical robustness. As a result, organizations are typically left with two approaches:
Application approach: Sprawl of AI assistants and point solutions
The first approach involves copilots, point solutions, and SaaS platforms, where AI agents are primarily seen as task assistants. For instance, many software vendors are now offering copilots that function as natural-language conversational assistants integrated into their existing platforms. Microsoft, for example, markets a product called “Power Virtual Agents,” which is a natural-language conversational design tool tailored for customer support teams. These solutions are popular among business teams because they’re quick to implement and often come with no-code tools, allowing users to build and customize their own agents.
However, these agents are typically limited to specific tasks and can’t support end-to-end workflows. This can lead to workflow fragmentation, where different agents are unable to communicate with each other. Additionally, these solutions can result in shadow IT, a lack of centralized governance, and potential security risks.
DIY approach: Autonomous AI agents at a cost
The second approach is more technical and involves hyperscalers, LLM research labs, and developer frameworks, where AI agents are viewed as autonomous reasoners. Hyperscalers like Amazon Bedrock and Google Vertex offer a wide range of options that allow for a DIY approach, enabling users to stitch together models, RAG pipelines, tools, and APIs. IT teams and professional engineers often favor these solutions due to the deep, complex customization they offer.
While this approach provides great flexibility and the ability to build a highly tailored stack, it’s also very expensive and time-consuming to develop and maintain. The rapid pace of technological advancements in the AI space can make it challenging to keep up, and updates from LLM research labs can introduce brittleness into the stack, with issues related to backward compatibility. Furthermore, the technical nature of these tools means that only technical personnel can use them, creating a bottleneck in IT and limiting the scalability of the solutions to non-technical users.
Unified approach: Centralized AI management
While both the application-led and DIY approaches have their advantages, neither can scale fast enough—or securely enough—to meet the growing demands of modern enterprises. That’s why a third approach is emerging: a unified, collaborative model that brings IT and business teams together to deploy AI agents.
With an end-to-end platform like WRITER, IT and business teams are equipped with shared tools to build, activate, and supervise AI agents—centralizing development, adoption, and governance in one place. Business teams contribute their domain knowledge and define the business logic, while IT ensures security, scalability, and reusable architectures. Together, they combine their expertise to co-build agents that are high-quality, aligned to real business needs, and built to scale.
By eliminating the trade-offs of siloed tools and custom stacks, the unified approach offers a more sustainable, balanced solution that aligns with the evolving needs of modern enterprises.
How agentic AI systems work in enterprise environments
Agentic AI systems have key components that enable autonomous decision-making and efficient task execution, which are essential for scaling enterprise operations.
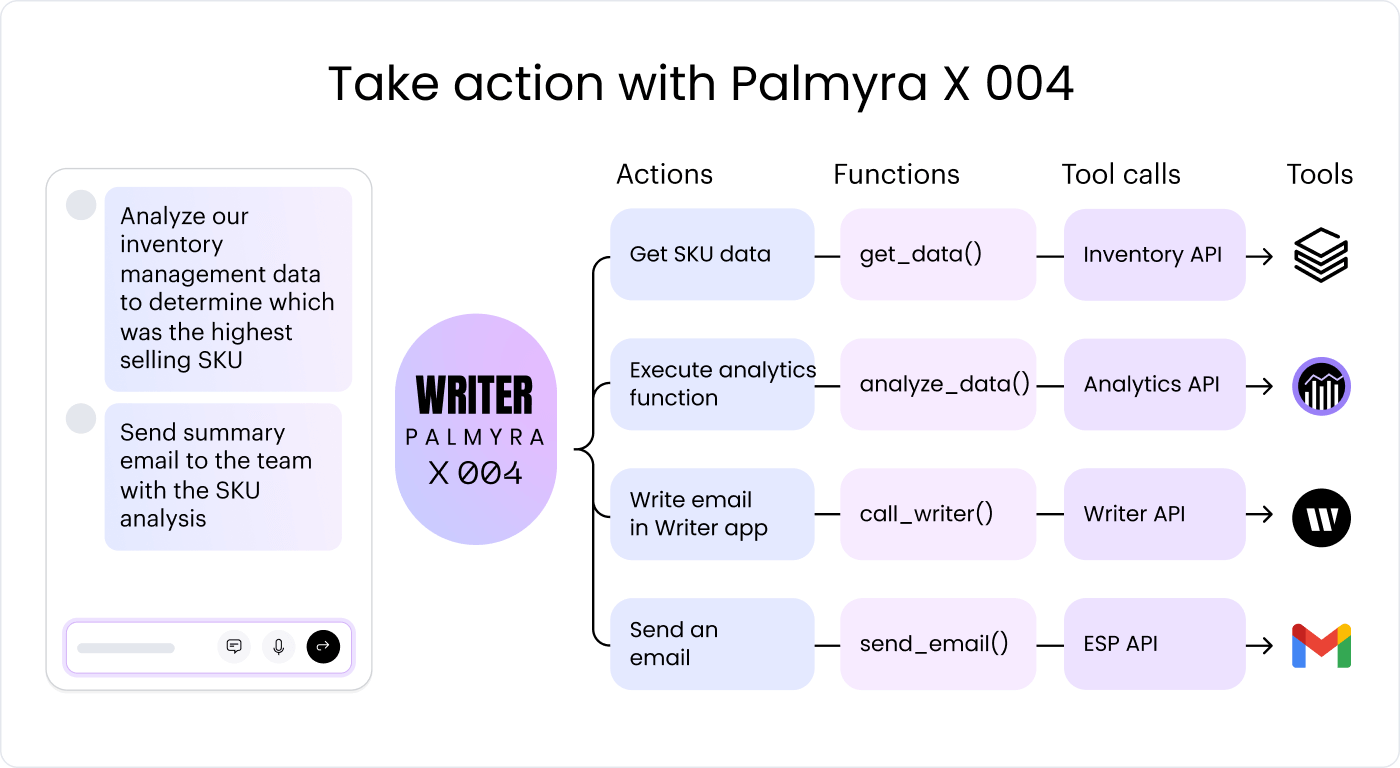
Here’s a breakdown of how these systems function:
- Large Language Model (LLM): An LLM is a crucial element that improves AI capabilities, including complex reasoning and automation. For example, the WRITER platform uses Palmyra LLMs to handle intricate workflows and achieve specific outcomes efficiently.
- Goal initialization and planning: AI agents require clearly defined goals and environments. Developers — who design and train them, teams that deploy them, and users who provide specific goals and tools — influence these systems.
- Task decomposition: AI agents break down complex goals into manageable tasks and subtasks, enhancing their ability to plan and execute effectively.
- Tool calling and reasoning: They use tools such as external datasets, web searches, APIs, and collaboration with other agents to gather necessary information, update their knowledge bases, and reassess their actions.
- Learning and adaptation: AI agents continuously learn from past interactions and adapt to increasingly complex challenges and changing user expectations. They “remember” experiences to improve future performance and provide personalized responses.
- Feedback mechanisms: They incorporate human users and other AI agents’ feedback to refine their responses and ensure alignment with the intended goals.
- Multi-agent collaboration: For complex tasks, AI agents collaborate with other agents to synthesize information and address knowledge gaps, thereby enhancing their overall capabilities and performance.
These components work together to create a robust system that can autonomously handle a wide range of tasks, making enterprise operations more efficient and effective.
The benefits of AI agents in the enterprise
Integrating AI agents into your enterprise can bring significant advantages beyond the obvious. Let’s explore how these agents can improve your operations:
Cost savings
Automating routine tasks: AI agents are great at handling repetitive tasks like data entry, scheduling, and basic customer inquiries. This automation reduces the need for human involvement, lowering labor costs. Plus, it frees your team to focus on more creative and strategic work.
Better resource allocation: By automating mundane tasks, you can redirect your people and other resources to high-impact projects that add more value to your business. This shift can lead to more innovative initiatives and better overall performance.
Improved efficiency
Round-the-clock operation: Unlike human employees, AI agents can work 24/7 without breaks. This continuous operation ensures your business stays responsive and productive at all times, helping you meet customer demands more effectively.
Handling multiple interactions: Intelligent agents can manage multiple customer interactions simultaneously, integrating data from various sources to enhance decision-making capabilities. This reduces wait times and increases throughput, especially in customer service, where quick and efficient interactions are key.
Fast data processing: AI agents can process large amounts of data quickly, providing timely analyses that are crucial for maintaining operational efficiency. This speed allows for quicker decision-making and more agile responses to market changes.
Better decision-making
Real-time data and insights: AI agents provide up-to-the-minute data, enabling more accurate and timely decisions. This real-time information can be a game-changer in fast-paced industries where quick, informed decisions are critical.
Data-driven insights: By analyzing patterns and trends from large datasets, AI agents help identify opportunities and predict future trends. These insights support strategic planning and can give your business a competitive edge by anticipating market shifts and customer needs.
Consistent responses: Consistently handling every decision or customer interaction reduces errors and enhances reliability. This consistency builds trust with customers and stakeholders, reinforcing your brand’s reputation for dependability.
Happier customers
Quick and accurate responses: AI agents provide quick, accurate, personalized responses, significantly improving the overall customer experience. Customers appreciate the efficiency and reliability of AI-driven interactions, leading to higher satisfaction rates and loyalty.
Scalability
Easy scaling: AI agents can easily handle increased volumes of interactions without needing a proportional increase in human resources. This scalability is particularly beneficial during peak periods or rapid growth phases, allowing your business to handle increased demand seamlessly.
By using AI agents, enterprises can achieve a level of efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and customer satisfaction that was previously unattainable. These benefits not only streamline operations but also position your business for sustained growth and success in a competitive market.
Examples of AI agent use cases by industry
AI agents are an emerging technology that can transform mission-critical workflows in various industries. Here’s a look at what’ll be possible across different sectors:
AI agents in financial services
Automated data entry and transaction processing: AI agents can handle data entry tasks and process transactions efficiently, guaranteeing compliance with regulatory standards. This automation saves time and reduces the risk of human error, making financial operations smoother and more reliable.
Improved advisory services: An autonomous AI agent for financial advisors can provide tailored recommendations and summarize client interactions, offering a more personalized and efficient service.
Fraud detection: By analyzing transaction patterns, AI agents can flag suspicious activities in real time, enhancing security measures. This proactive approach helps financial institutions protect their customers and maintain trust.

Generative AI use cases for financial services
Get started
AI agents in healthcare and life sciences
Patient record management: AI agents can analyze vast amounts of medical and patient data to enhance care decisions and automate administrative tasks. They can organize and update patient records, schedule appointments, and manage billing processes. This automation frees healthcare professionals to focus on patient care, improving overall efficiency and accuracy.
Clinical trial management: AI agents can expedite clinical trial management by aiding in patient recruitment and screening, monitoring data in real-time for compliance, and enhancing patient engagement through personalized communication and symptom tracking. This technology accelerates the development of new treatments and can help improve patient care.
The big book of generative AI use cases for healthcare payors
Get started
AI agents in retail and consumer packaged goods (CPG)
Inventory management: AI agents can predict demand and automate restocking processes, optimizing inventory levels. This ensures that shelves are always stocked with the right products, reducing the risk of stockouts and overstocking.
Customer returns and refunds: AI agents can efficiently process returns and refunds, improving operational efficiency. This automation enhances the customer experience by making the return process quicker and more convenient.
Marketing campaign management: AI agents can streamline the management of marketing campaigns and generate promotional content, helping to keep consumers engaged and informed about new products. This capability allows retailers to create more targeted and effective marketing strategies.

Retail personalization with WRITER
Get started
AI agents in insurance
Claims processing automation: AI agents can reduce the time and effort required to assess and approve claims by automating the claims processing workflow. This automation speeds up the claims process, improving customer satisfaction and reducing operational costs.
Risk analysis and underwriting: AI agents can analyze risk factors and help determine appropriate premiums, streamlining the underwriting process. This capability allows insurers to make more informed decisions and offer more competitive rates.

Generative AI insurance use cases
Get started
By leveraging AI agents, industries can significantly improve efficiency, accuracy, and customer satisfaction. As this technology continues to evolve, the possibilities for its application are only set to grow.
The challenges of implementing AI agents in the workplace
Bringing AI agents into the workplace can be a game-changer, but it’s not all smooth sailing. There are hurdles to overcome, from managing enterprise data governance to employee pushback. Let’s dive into the key challenges and how to tackle them.
Data governance and security
AI agents thrive on data — often sensitive data. That raises serious privacy concerns and the specter of data breaches. To build trust and stay compliant, robust data protection measures are a must.
Businesses need to ensure their AI agents follow the rules. This means staying on top of relevant laws and regulations, which can be a moving target depending on the region and industry. Keeping up with the legal landscape is crucial to avoid potential pitfalls.
The talent gap
Deploying and maintaining AI agents requires specialized skills in AI and machine learning. These advanced software engineering skills are in high demand but in short supply. Investing in training and development can help bridge this gap.
AI tech evolves at a breakneck pace, so ongoing education is essential. Fostering a culture of continuous learning helps employees keep up with the latest advancements.
The cost and complexity conundrum
AI agents require a significant upfront investment in infrastructure, software, and training. Careful planning and budgeting can help manage these costs effectively.
Integrating AI agents with existing systems can be complex and disruptive. A phased approach to implementation can mitigate these risks and smooth the transition.
Multi-agent systems and human intervention
In multi-agent systems, dependencies can lead to system-wide failures if one agent malfunctions. Robust testing and monitoring are key to identifying and addressing potential issues early.
Multi-agent systems can be more susceptible to cyber-attacks. Strong security protocols and regular updates are essential to enhance protection.
Ethical dilemmas in AI decision-making
If not properly designed and monitored, AI agents can inadvertently perpetuate or even exacerbate biases. Guaranteeing fairness and transparency in AI algorithms is crucial for ethical decision-making.
AI agents often operate in a black box, raising concerns about accountability. Establishing clear guidelines and audit trails can enhance transparency and build trust.
Retraining and upskilling
As AI agents take over routine tasks, employees should get retrained for more complex and strategic roles. Comprehensive training programs can help employees adapt to these changes.
Innovative companies understand the importance of fostering a culture of continuous learning and adaptation. Employees may resist AI implementation due to fears of job displacement or discomfort with new technologies. Open communication and support can help alleviate these concerns and foster a positive transition.
By tackling these challenges head-on, businesses can tap into the full potential of AI agents while providing a smooth and responsible implementation. It’s not just about the tech — it’s about the people and processes that make it work.
Strategies for successful AI agent deployment
Deploying AI agents in the enterprise world can be a complex task, but with the right strategies, it can be a game-changer. Enterprises can develop their own AI agents using resources like WRITER AI Studio, a suite of no-code and developer tools for integrating enterprise-grade generative AI directly into your own tools and services. Here are some approaches to ensure your AI agents hit the ground running.
Establish use cases with mission-critical business logic: Focus on understanding your existing processes and making sure agents are ready to join those workflows.
Define clear goals and environments: Collaborate between developers, deployers, and users to ensure the agent understands its objectives and available tools.
Equip agents with relevant, fresh data: Build a pipeline that brings fresh data related to your specific use cases.
Identify people who understand your use cases and workflows: Figure out who’s deeply familiar with your use cases, has the right technical skills, and understands the business processes.
Implement feedback loops: Use human-in-the-loop (HITL) systems to refine performance and align with user expectations, improving accuracy and personalization.
Ensure human oversight: Maintain control and prevent unintended consequences by requiring human approval for critical decisions.
Use unique identifiers and activity logs: Trace agent actions for accountability and transparency, helping identify errors or areas for improvement.
Enable iterative learning and adaptation: Allow agents to learn from past interactions and adapt to new environments, enhancing their ability to handle complex tasks.
Manage risks effectively: Address potential issues like infinite feedback loops and computational complexity with interruptibility and monitoring systems.
Manage your organization’s ability to handle change: Address your organization’s capacity for change and understand how end-users find value in the technology.
By following these tips, enterprises can successfully deploy AI agents to automate tasks, enhance decision-making, and improve overall business operations.
WRITER: The end-to-end platform that unites IT and business
At WRITER, we’re not just imagining a world where AI agents transform the enterprise — we’re building it, step by step, by focusing on several key areas.

Core technology engineered exclusively for enterprises
WRITER is the only AI research lab 100% focused on enterprise needs — not consumer products or research papers. Everything we build is designed to make agentic AI a reality for businesses. Our Palmyra family of LLMs is purpose-built on the latest transformer architecture and continuously trained for enterprise-grade accuracy, performance, and cost efficiency. Paired with our proprietary graph-based Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG), WRITER delivers fast, context-rich outputs grounded in your business knowledge.
Deep partnership to accelerate your AI transformation
We understand that in the enterprise, generative AI isn’t just a technology shift — it’s an organizational one. That’s why we partner closely with customers not only to build agents, but to roll them out, refine them, and drive lasting adoption. Our team brings the experience and hands-on support needed to turn AI into tangible business impact — from P&L improvements to smarter workflows and empowered teams.
Operational transformation
Our platform’s goal is to automate mission-critical workflows, increase tool usage, and improve the observability and reasoning capabilities that will help your enterprise transform its operations and drive innovation.
Our strategic approach positions WRITER as a leader in creating an end-to-end enterprise platform that equips companies with easy-to-implement, effective AI agents.
Ready to transform your enterprise?
Now that you’ve explored the power of AI agents, it’s time to take the next step. Whether you’re a developer looking to integrate cutting-edge AI into your systems or a business leader seeking to drive operational transformation, WRITER is here to support you.
Get started today by reaching out to our team. Let’s discuss how WRITER can tailor AI solutions to meet your specific needs and help your enterprise thrive in the future of work. Together, we can make AI-driven innovation a reality for your business.